Search results
Search for "surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs)" in Full Text gives 14 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Plasmonic nanotechnology for photothermal applications – an evaluation
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 380–419, doi:10.3762/bjnano.14.33

- films, they are propagating oscillations termed surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs)). A plasmon in LSPR can be visualized as a quasiparticle confined to the volume of the nanoparticle [27]. The resulting confinement of the absorbed incident electromagnetic radiation within the nanoparticle thus means an
Characterisation of a micrometer-scale active plasmonic element by means of complementary computational and experimental methods
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 110–122, doi:10.3762/bjnano.14.12

- imaging technologies and as modulators in optoelectronic couplers for photonic circuits. Finite element method (FEM) simulations are used to validate both experimental approaches, allowing for cross-verification of results and giving greater insight into the underlying physical phenomena. Surface plasmon
- polaritons (SPPs) are mixed states of photons and electron density waves propagating along the interface between a conductor and a dielectric. As a result of this phenomenon, an electric field strongly confined in the z-direction is produced at the interface. As direct excitation of a smooth metallic surface
Tunable high-quality-factor absorption in a graphene monolayer based on quasi-bound states in the continuum
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 675–681, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.59

- structure, graphene supports much stronger binding of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) with less loss, which leads to a longer propagation distance compared with traditional metal SPPs [35]. In addition, its conductivity can be dynamically controlled by chemical doping or electrostatic fields owing to the
The influence of an interfacial hBN layer on the fluorescence of an organic molecule
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1663–1684, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.149

- additional enhancement [46]. According to the electromagnetic mechanism, on a rough surface, surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) can also be excited by the incident light. The surface plasmons are located in the vicinity of surface defects, such as protrusions. The field enhancement at these defects leads to
Optically and electrically driven nanoantennas
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1542–1545, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.136

- the feed-gap is shown to couple to propagating modes in waveguides with up to 30% efficiency. Making use of propagating surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs), directional light beams are created in [57]. The SPPs are excited by inelastic tunneling from a scanning probe. The probe is positioned in the
Plasmonic nanosensor based on multiple independently tunable Fano resonances
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2527–2537, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.243

- nanosensors, optical splitters, filters, optical switches, nonlinear photonic and slow-light devices. Keywords: Fano resonance; metal–dielectric–metal (MDM) waveguide; nanosensor; on-chip plasmonic structures; surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs); Introduction Surface plasmon polariton (SPP) is a unique
Multiple Fano resonances with flexible tunablity based on symmetry-breaking resonators
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2459–2467, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.236

- reflectance). In addition to PhC waveguides, metal–dielectric–metal (MDM) waveguides are very attractive for researchers because they can support surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) and allow for the control of light at the subwavelength scale. MDM waveguides provide an effective approach to chip-scale photonic
Magnetic-field sensor with self-reference characteristic based on a magnetic fluid and independent plasmonic dual resonances
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 247–255, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.23
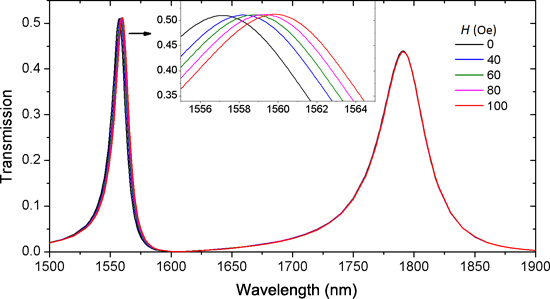
- fabrication and compactness. In recent years, compact optical devices based on surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) have been reported. SPPs propagate along the dielectric–metal interface with the amplitudes decaying exponentially into both sides [16]. The deep subwavelength confinement of SPPs leads to the
Directional light beams by design from electrically driven elliptical slit antennas
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2361–2371, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.221

- , bull’s-eye, nanoparticle dimer, or wire antennas), coupled in the near field (or incorporating in their design) an electrically driven nanosource of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs, light waves coupled to electron density oscillations at a metal–dielectric interface). In particular, the electrical SPP
Cathodoluminescence as a probe of the optical properties of resonant apertures in a metallic film
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1491–1500, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.140

- maximum in the back-emission spectrum are consistent with only weak penetration into the cavity and the resonance being associated with a resonance of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) of the approximately triangular region on the surface of the film defined by the apertures. Although a mode with radially
Near-field surface plasmon field enhancement induced by rippled surfaces
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 956–967, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.97

- scanning near-field optical microscopy. Keywords: aperture scanning near-field optical microscopy; gold rippled surface; localized hot spots; metal–dielectric−metal nanogaps; surface plasmon resonance; Introduction Metal nanostructures capable of producing localized surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are
Near-field visualization of plasmonic lenses: an overall analysis of characterization errors
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2069–2077, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.211

- nanophotonic devices. Keywords: characterization; nanofabrication; near-field; plasmonic lenses; plasmonic structures; Introduction The characteristics of nanophotonic devices that are based on surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are appealing because of the extraordinary transmission in free space [1][2][3][4
Synergic combination of the sol–gel method with dip coating for plasmonic devices
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 500–507, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.52

- ) are extremely sensitive to the refractive index of the dielectric medium [1][2][9] and the two plasmons modes, surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) and localized surface plasmons (LSPs), can be used for sensor applications [8][10][11]. However, in order to use this technology for sensing of a specific
k-space imaging of the eigenmodes of sharp gold tapers for scanning near-field optical microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 603–610, doi:10.3762/bjnano.4.67

- nanostructures support collective oscillations of the electron gas, which couple strongly to light. At extended metal–dielectric interfaces, the resulting surface-bound modes, termed surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs), may propagate along the interface. At geometric singularities, i.e., in regions of deep

































































































































